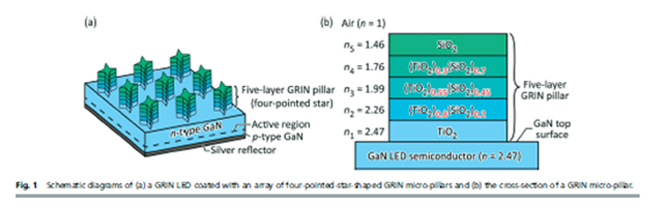
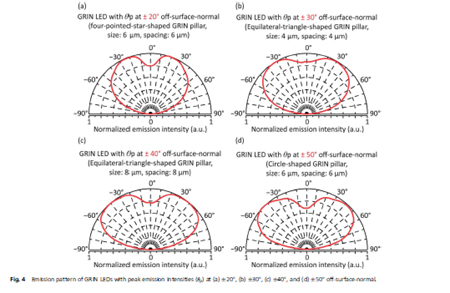
Solid-state light sources that are efficient and capable of high power: Solid-state (semiconductor) light sources are revolutionizing an increasing number of applications. Whereas the efficiency of conventional incandescent and fluorescent lights is limited by fundamental factors that cannot be overcome, the efficiency of solid -state sources based on light-emitting diodes is limited only by human creativity and imagination. The high efficiency of solid-state sources already provides energy savings and environmental benefits in a number of applications.
Moreover, solid-state sources also offer controllability of their spectral power distribution, spatial distribution, color temperature, temporal modulation, and polarization properties. Such ‘smartness’ of the light source can adjust to specific environments and requirements, a property that could result in tremendous benefits in lighting, automobiles, transportation, communication, imaging, agriculture, and medicine.
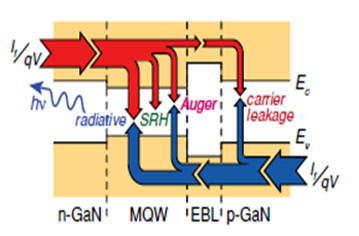
In spite of the huge improvement of solid-state light source during the last two decades, there are still a lot of technical challenges if it is aimed to the final goal of ‘smart’ lighting. They are, so called, the green gap, efficiency droop, low efficient DUV, and extraction efficiency problems.
herefore, in this field of the research topic, I would like to touch physical origins and mechanisms which rule each technical challenge, so resulting in better understanding and performance of the materials/devices.